Genomics
Institute
glossary
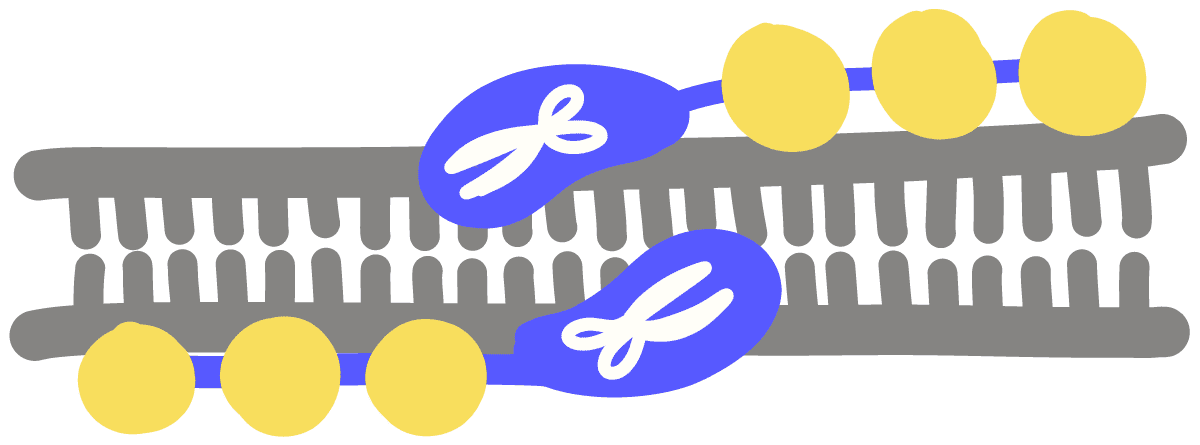
Zinc-finger nuclease (ZFN)
A genetic engineering tool wherein one portion of the protein recognizes a specific DNA sequence and another part cuts DNA. Made by attaching a series of smaller DNA-binding domains together to recognize a longer DNA sequence. This DNA-binding domain is fused to a nuclease that will cut nearby DNA. Like CRISPR-Cas9 and TALENs, it can be used to alter DNA sequences.
« Back to Glossary Index