Genomics
Institute
glossary
Enzyme
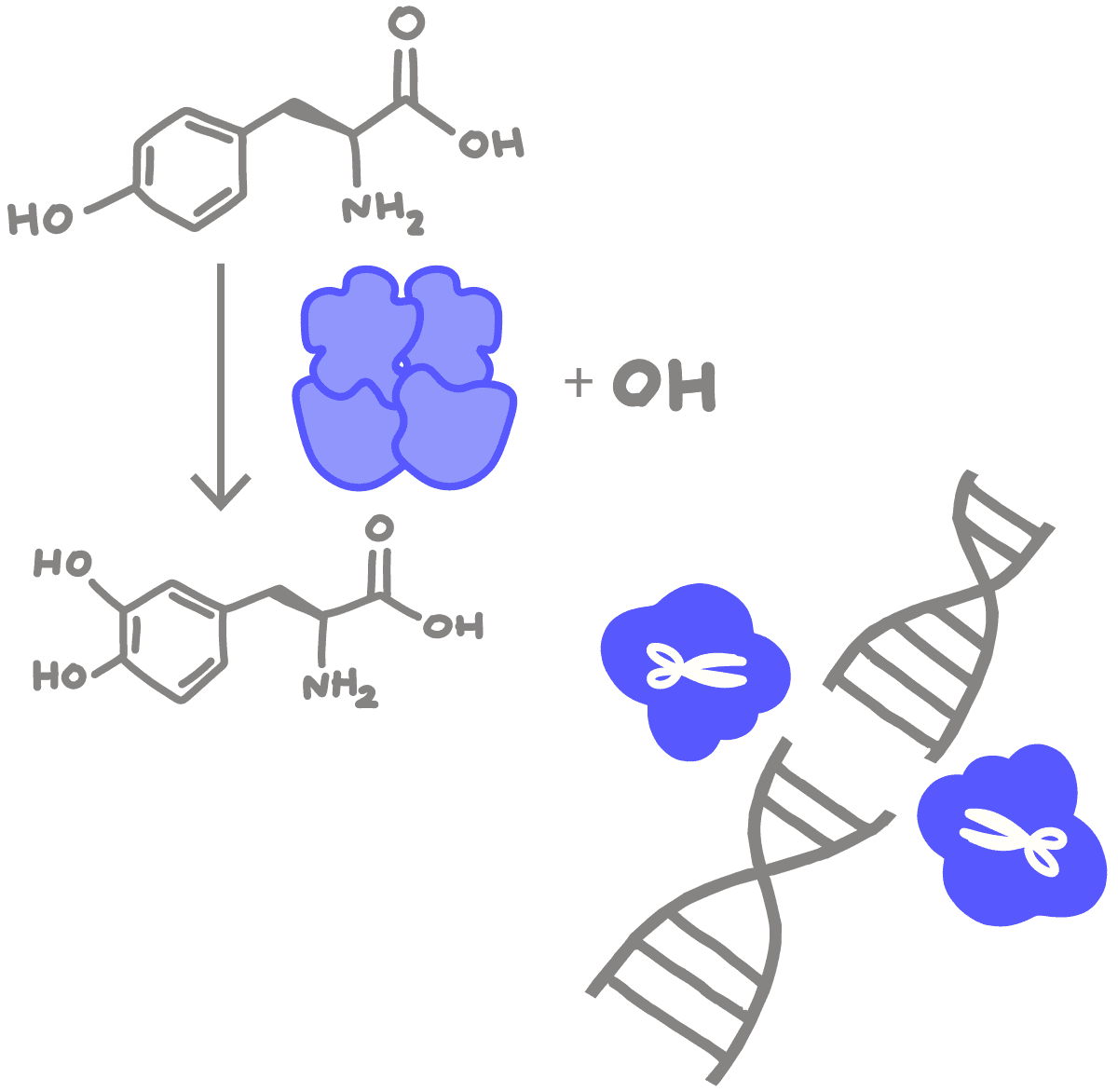
A molecule, typically a protein, that causes or catalyzes a chemical change. Usually an enzyme’s name describes a molecule involved in the activity it performs and ends with the suffix -ase. For example, lactase is a well-known enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in milk. Cas9 is a nuclease, an enzyme that breaks apart the backbone of nucleic acids (RNA or DNA).
« Back to Glossary Index