Frequent, rapid testing for COVID-19 is critical to controlling the spread of outbreaks, especially as new, more transmissible variants emerge.
While today’s gold standard COVID-19 diagnostic test, which uses qRT-PCR — quantitative reverse-transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) — is extremely sensitive, detecting down to one copy of RNA per microliter, it requires specialized equipment, a runtime of several hours and a centralized laboratory facility. As a result, testing typically takes at least one to two days.
A research team led by scientists in the labs of Jennifer Doudna, David Savage and Patrick Hsu at the University of California, Berkeley, is aiming to develop a diagnostic test that is much faster and easier to deploy than qRT-PCR. It has now combined two different types of CRISPR enzymes to create an assay that can detect small amounts of viral RNA in less than an hour. Doudna shared the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for invention of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing.
While the new technique is not yet at the stage where it rivals the sensitivity of qRT-PCR, which can detect just a few copies of the virus per microliter of liquid, it is already able to pick up levels of viral RNA — about 30 copies per microliter — sufficient to be used to surveil the population and limit the spread of infections.
“You don’t need the sensitivity of PCR to basically catch and diagnose COVID-19 in the community, if the test’s convenient enough and fast enough,” said co-author David Savage, professor of Molecular and Cell Biology. “Our hope was to drive the biochemistry as far as possible to the point where you could imagine a very convenient format in a setting where you can get tested every day, say, at the entrance to work.”
The researchers will report their results online August 5 in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
Several CRISPR-based assays have been authorized for emergency use by the Food and Drug Administration, but all require an initial step in which the viral RNA is amplified so that the detection signal — which involves release of a fluorescent molecule that glows under blue light — is bright enough to see. While this initial amplification increases the test’s sensitivity to a similar level as qRT-PCR, it also introduces steps that make the test more difficult to carry out outside of a laboratory.
The UC Berkeley-led team sought to reach a useful sensitivity and speed without sacrificing the simplicity of the assay.

Aside from having an added step, another disadvantage of initial amplification is that, because it makes billions of copies of viral RNA, there is a greater chance of cross-contamination across patient samples. The new technique developed by the team flips this around and instead boosts the fluorescent signal, eliminating a major source of cross-contamination.“For point of care applications, you want to have a rapid response so that people can quickly know if they’re infected or not, before you get on a flight, for example, or go visit relatives,” said team leader Tina Liu, a research scientist in Doudna’s lab at the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI), a CRISPR-focused center involving UC Berkeley and UC San Francisco scientists.
The amplification-free technique, which they term Fast Integrated Nuclease Detection In Tandem (FIND-IT), could enable quick and inexpensive diagnostic tests for many other infectious diseases.
“While we did start this project for the express purpose of impacting COVID-19, I think this particular technique could be applicable to more than just this pandemic because, ultimately, CRISPR is programable,” Liu said. “So, you could load the CRISPR enzyme with a sequence targeting flu virus or HIV virus or any type of RNA virus, and the system has the potential to work in the same way. This paper really establishes that this biochemistry is a simpler way to detect RNA and has the capability to detect that RNA in a sensitive and fast time frame that could be amenable for future applications in point of care diagnostics.”
The researchers are currently in the process of building such a diagnostic using FIND-IT, which would include steps to collect and process samples and to run the assay on a compact microfluidic device.
Employing tandem Cas proteins
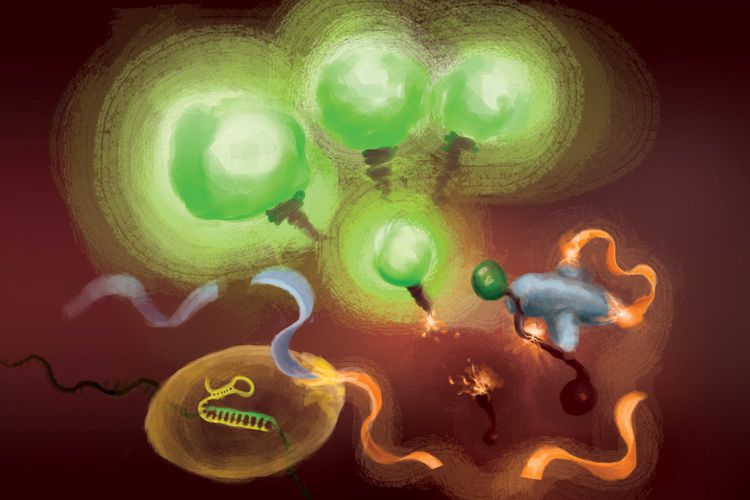
To remove target amplification from the equation, the team employed a CRISPR enzyme — Cas13 — to first detect the viral RNA, and another type of Cas protein, called Csm6, to amplify the fluorescence signal.
Cas13 is a general purpose scissors for cutting RNA; once it binds to its target sequence, specified by a guide RNA, it is primed to cut a broad range of other RNA molecules. This target-triggered cutting activity can be harnessed to couple detection of a specific RNA sequence to release of a fluorescent reporter molecule. However, on its own, Cas13 can require hours to generate a detectable signal when very low amounts of target RNA are present.
Liu’s insight was to use Csm6 to amplify the effect of Cas13. Csm6 is a CRISPR enzyme that senses the presence of small rings of RNA and becomes activated to cut a broad range of RNA molecules in cells.
To boost Cas13 detection, she and her colleagues designed a specially engineered activator molecule that gets cut when Cas13 detects viral RNA. A fragment of this molecule can bind to and trigger Csm6 to cut and release a bright fluorescent molecule from a piece of RNA. Normally, the activator molecule is quickly broken down by Csm6, thus limiting the amount of fluorescent signal it can generate. Liu and her colleagues devised a way to chemically modify the activator so that it is protected from degradation and can supercharge Csm6 to repeatedly cut and release fluorescent molecules linked to RNA. This results in a sensitivity that is 100 times better than the original activator.
“When Cas13 gets activated, it cleaves this small activator, removing a segment that protects it,” Liu said. “Now that it’s liberated, it can activate lots of different molecules of that second enzyme, Csm6. And so, one target recognized by Cas13 doesn’t just lead to activation of its own RNA-cutting ability; it leads to the generation of many more active enzymes that can each then cleave even more fluorescent reporters.”
The team of researchers also incorporated an optimized combination of guide RNAs that enables more sensitive recognition of the viral RNA by Cas13. When this was combined with Csm6 and its activator, the team was able to detect down to 31 copies per microliter of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in as little as 20 minutes.
The researchers also added extracted RNA from patient samples to the FIND-IT assay in a microfluidic cartridge, to see if this assay could be adapted to run on a portable device. Using a small device with a camera, they could detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA extracted from patient samples at a sensitivity that would capture COVID-19 infections at their peak.
“This tandem nuclease approach — Cas13 plus Csm6 — combines everything into a single reaction at a single temperature, 37 degrees Celsius, so it does not require high temperature heating or multiple steps, as is necessary for other diagnostic techniques,” Liu said. “I think this opens up opportunities for faster, simpler tests that can reach a comparable sensitivity to other current techniques and could potentially reach even higher sensitivities in the future.”
The development of this amplification-free method for RNA detection resulted from a reorientation of research within IGI when the pandemic began toward problems of COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment. Ultimately, five labs at UC Berkeley and two labs at UCSF became involved in this research project, one of many within the IGI.
“When we started this, we had hopes of creating something that reached parity with PCR, but didn’t require amplification — that would be the dream,” said Savage, who was principal investigator for the project. “And from a sensitivity perspective, we had about a ten thousandfold gap to jump. We’ve made it about a thousandfold; we’ve driven it down about three orders of magnitude. So, we’re almost there. Last April, when we were really starting to map it out, that seemed almost impossible.”
The work was supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (N66001-20-2-4033). Co-authors of the paper include members of the labs of Jennifer Doudna, David Savage, Patrick Hsu, Liana Lareau and Daniel Fletcher at UC Berkeley; Gavin Knott at Monash University in Australia; Melanie Ott and Katherine Pollard at the Gladstone Institutes and UCSF; and Ming Tan at Wainamics, a research and development firm in Pleasanton, California, that produces microfluidic devices. Doudna, IGI’s founder and currently president and chair of the IGI governance board, is the Li Ka Shing Chancellor’s Chair at UC Berkeley and a professor of chemistry and of molecular and cell biology. Hsu, Lareau and Fletcher are faculty in the Department of Bioengineering.
This story was originally published by the UC Berkeley News.
Learn more:
- Accelerated RNA detection using tandem CRISPR nucleases (Nature Chemical Biology)
- New CRISPR-based COVID-19 test uses smartphone cameras to spot virus RNA (December 2020)
Media contact: Andy Murdock, andymurdock@berkeley.edu




